Investment appraisal
Investment appraisal is a number of methods used to classify the attractiveness of an investment.
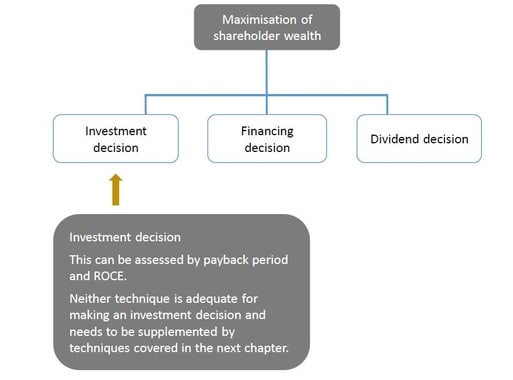
Investment appraisal actually from Investment decision, Which project has to finance, the Business has to make the investment, And you have to pick up which project I best for investment
- Capital expenditure results in the acquisition of non-current assets or an improvement in their earning capacity.
- It is not charged as an expense in the statement of profit or loss; it appears as a non-current asset in the statement of financial position.
- Capital expenditure and income arising from it usually occur in different accounting periods, so special techniques are needed to evaluate it.
- The underlying motive is generally to assess the impact on shareholder wealth
Investment appraisal for Commercial organizations
Investment by commercial organizations might include investment in:
- Plant and machinery
- Research and development
- Advertising
- Warehouse facilities
Investment by the commercial sector is generally based on financial considerations alone.
Investment appraisal for Not For-profit organizations
Evaluation of investment by not for profit organizations is more challenging:
- Most not-for-profit organizations’ investments are not made with the intention of earning a financial return.
- As well as considering financial costs and financial benefits, social costs and social benefits are important.
- The cost of capital that is applied to project cash flows by the public sector will be
- one that is determined by the government.
Capital Rationing
It is a situation in which limited funds are available to invest in positive NPV Projects
Budget limits or constraints can arise from:
- Soft capital rationing, where constraints are imposed internally by management. ( Eg via a capital expenditure budget.)
- Hard capital rationing, where constraints are imposed by external factors,
- such as restrictions on the amount of external financing available.
Soft Capital Rationing Vs Hard Capital Rationing
| Soft Capital Rationing | Hard Capital Rationing |
| It is a situation in which limited funds are available to invest in a positive NPV project because of internal Factor’s | It is a situation in which limited funds are available to invest in a positive NPV project because of External Factors |
| Management may be reluctant to issue further shares because of dilution in the control of existing shareholders. | The company can not raise further funds by issuing shares because stock prices are depressed in the stock exchange |
| Management may be unwilling to issue further share because of dilution in EPS (Earning per share) | There may be a restriction on bank lending due to government controls |
| The company has the policy to finance all new projects only from Retain Earnings. | The lending institution may consider your company too risky for further lending |
| Management may not raise further debts because of fixed the commitment of interest payments | The cost of funds for arranging a new loan is too high |
Both types of constraints mean that investment has to be carefully planned to ensure the best use of funds.
Capital Budgeting Cycle
- Idea generation
- Project Screening
- Availability of funds
- Link to the strategic objective
- Government Rejection/Mandatory
- Financial Analysis
- Initial Method
Simple payback period
ARR - Advanced Method
NPV
Discounted Payback period
IRR
- Initial Method
- Non-Financial Analysis
- Political factors
- Ethical issues
- investment issues
- social issues
- Legal issues
- Approval (e.g From the board of directors)
- Implementation e.g Project Manager
- Ongoing Monitoring
- Post completion
Why Project screening – a qualitative analysis
- What is the purpose of the project?
- Does it ‘fit’ with the organization’s long-term objectives?
- Is it a mandatory investment eg to comply with laws?
- What resources are required eg money, labor?
- Do we have the necessary management expertise?
- Does the project expose the organization to high risk?
- How long will the project last?
- What factors are key to their success?
- Have all possible alternatives been considered?
Financial analysis during Investment appraisal
Will use the preferred investment appraisal techniques.
- What cash flows/profits arise from the project and when?
- Has inflation been considered in the estimates?
- What are the results of the financial appraisal?
- What risk analysis has been done and its results?
- How have non-tangible benefits been assessed?
Intangible costs and benefits during Investment appraisal
In addition to easily quantified financial benefits there might also be important intangible, non-quantifiable effects:
- Greater customer satisfaction (eg because of a computerized sales and delivery service).
- Better recognition because of an improved website.
- Improved staff morale from working with higher-quality assets or better systems.
- Better decision-making from better information systems.
Hard to quantify does not mean ‘not important’
Read More:
Financial Management
Facebook
- Inflation
- Taxation
- Working capital
- Relevant/irrelevant cashflows
- Fixed appraisal horizon