AUDIT RISK and Auditor Response
AUDIT RISK and Auditor Response
Importance of AUDIT RISK and Auditor Response assessment

1. Assessing engagement risks at the planning stage, will ensure that attention is focused early on the areas most likely to cause material misstatements.
2. It will help the auditor to fully understand the entity, which is vital for an effective audit.
3. Any unusual transactions or balances would also be identified early so that these could be addressed in a timely manner.
4. Assessing risks early is an efficient practice by auditors. The auditors will only focus their time and effort on key areas as opposed to transactions or balances that might be immaterial or unlikely to contain errors.
5. As well as assessing risk early should ensure that the most appropriate or most experienced team is selected and staff allocated to higher risk audits and high-risk balances.
6. A thorough risk summary should sequentially reduce the risk of an inappropriate audit opinion being presented.
7. It should enable the auditor to have a good understanding of the risks of fraud, money laundering, etc.
8. Assessing risk should enable the auditor to assess whether the client is a going concern.
Audit Risk
‘The risk that the auditor expresses an inappropriate audit opinion meanwhile the financial statements are materially misstated. Audit risk is a reception of the risks of material misstatement and detection risk’
The formula for the audit risk model is:
Audit Risk = Risk of material misstatement in the financial statements x Detection Risk
Risk of material misstatement= Inherent Risk * Control Risk
Audit Risk Explained
Audit risk is the risk where financial statements are materially misstated and the auditor expresses an inappropriate audit opinion
The risk of material misstatement contains two components, control risk, and inherent risk.
The risk of material misstatement in the financial statements explained
The risk of material misstatement has further two components, inherent risk, and control risk.
Inherent Risk:
Definition: The susceptibility of an assertion about an account balance disclosure or class of transaction to a mistake that could be material, either individually or when complied with other misstatements, before consideration of any other relating controls.
Inherent risk describes something about the nature of a business or its transactions that makes it particularly susceptible to material misstatements.
Inherent risk is affected by the nature of an entity’s business and factors that can result in an increase include:
– Changes in the industry it operates in.
– Operations that are subject to a high degree of regulation.
– Going concern and liquidity issues also the loss of significant customers.
– offering or Developing new products or services, or moving into new lines of business.
– Expanding into new locations.
– Application of new accounting standards.
– Accounting measurements that involve complex processes.
– Transactions or events that involve significant accounting estimates.
– Pending litigation and contingent liabilities.
Control Risk
Definition: The risk that a misstatement that can occur in an assertion about an account balance, class of transaction, or disclosure and that could be material, either individually or when complied with other misstatements, will not be prevented, corrected, or detected, on a timely basis by the entity’s internal control system.
It is the risk that an organization’s internal control systems do not adequately protect the organization either because they have not been adequately designed and/or implemented.
The following factors can be the reason for an increase in control risk:
– Lack of staff with appropriate accounting and financial reporting skills.
– Changes in key staff including the departure of key management.
– Deficiencies in internal control, especially those not addressed by management (outsource).
– Changes in the information technology (IT) environment.
– Installation of significant new IT systems related to financial reporting( Transferring to the new system).
Auditor has no control over the extent of either inherent or control risk; these are risks related by the entity subject to audit. However, Auditor has to assess them in the process of determining the extent of the detailed substantive procedures during the audit.
Detection Risk Explained
Definition= The procedures auditor performs to minimize audit risk to a certain low level will not detect a misstatement that exists and that can be material, either individually or when complied with other misstatements. Detection risk is affected by sampling & non-sampling risk.
Detection risk is the risk that the auditor’s procedures fail to detect a material misstatement.
Detection risk is affected by sampling and non-sampling risk and factors which can result in an increase can be following
– Inadequate planning.
– Inappropriate assignment of staff to the engagement team.
– Failing to apply professional skepticism.
– Inadequate supervision and review of the audit work performed.
– Incorrect sampling techniques were performed.
– Incorrect sample sizes
Detection risk includes sampling risk and non-sampling risk ( these are explained in detail with the topic of sampling- below is an overview).
Sampling risk: The sample is not representative of the population
Non-sampling risk = auditor’s procedures or the conclusion reached are incorrect.
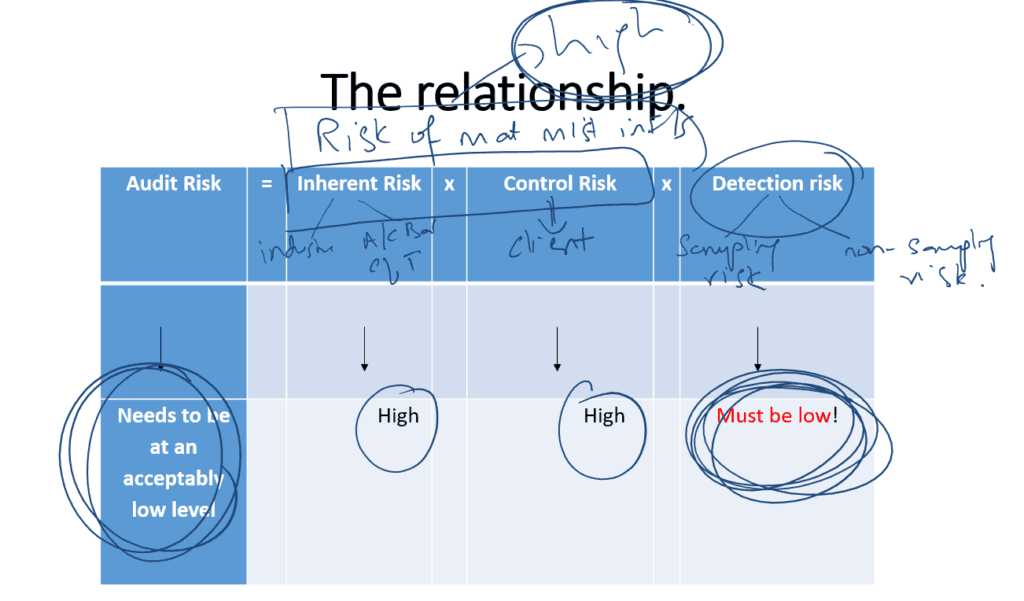
Audit Risk
=(Inherent Risk) x (Control Risk) x (Detection risk)
- Audit Risk Needs to be at an acceptably low level
- Inherent Risk= High
- Control Risk= High
- Detection Risk= Must be below!
The audit risk model used by auditors,
stated that for a given level of audit risk, the acceptable level of detection risk bears an inverse relationship to the assessment of the risk of material misstatement in Financial Statements.
For example, on an audit assignment where the risk of material misstatement has been assessed as high, in order to achieve a low level of audit risk, detection risk must be set as low as possible. In these circumstances, the auditor would need to handle an appropriate level of
resources to the testing of the assertion in question.
This will comprise adequate planning, proper assignment of staff, the application of professional skepticism and supervision, and a review of the audit work performed by the auditor.
Read More: Analytical Procedures
AUDIT RISK and Auditor Response
AUDIT RISK and Auditor Response

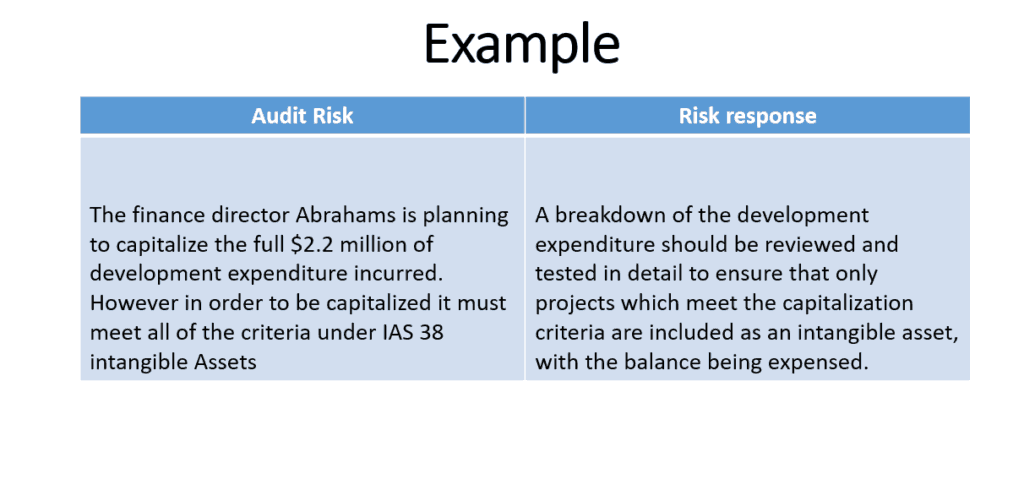
Audit Risk Examples From Audit and Assurance past exams
These are key examples of audit risk, repeated in papers very frequently
Solve them by yourself, if need our help, let us know in the comment section.
then we can upload a solved version of these examples for you.